Connecting to a Docker Container via SSH
In this tutorial, we will show how to connect to a Ubuntu Docker container via SSH. Note that some images may containing portions blacked out for security purposes.
0. Creating the Docker container
Run the following command to create a new Docker container with the Ubuntu image publishing port 2200 on 22 in our Ubuntu machine.
docker run --name test -p 2200:22 -t -i ubuntu /bin/bash
Be sure to give root a password using
passwd
1. Updating, upgrading, and installing openSSH-server and nano
Now that we have the container created and running, we will update and upgrade apt.
apt update && apt upgrade
Then we will need to install openssh-server.
apt install openssh-server
Now install nano.
apt install nano
2. Installing and adding a new user to sudo
When communicating remotely with any machine, security is a top priority. It is more secure to interface with the machine through a new user rather than root. With this, you can manage and restrict the permissions of the user, making your machine and data more secure.
Before creating a new user, we will install sudo which stands for “superuser do” or “substitute user”.
apt install sudo
Next we will create the new user.
sudo adduser USERNAME
We call this user ‘patrick’. You will be prompted to give patrick a password along with some other information that is optional. Next we will add patrick to the sudo group giving him sudo access.
usermod -aG sudo patrick
Now to switch to patrick (and between users) use
su patrick
Now whenever you want to run a command that requires sudo permissions, just prepend sudo.
3. Starting and stopping SSH
Switch back to the root user. We will now begin the process of enabling SSH. After installing openssh-server, you will be able to use
service --status-all
which will display the services and available and whether they are active. For example, this is what you should see if SSH is inactive.
[ - ] dbus
[ ? ] hwclock.sh
[ - ] procps
[ - ] ssh
to active SSH, type
service ssh start
then follow that by service --status-all and you should see the following.
[ - ] dbus
[ ? ] hwclock.sh
[ - ] procps
[ + ] ssh
Before we are able to SSH into the container, we need allow for us to connect to root in the SSH config file.
THIS IS OPTIONAL. WE DO NOT NEED TO ENABLE ROOT LOGIN. THIS IS ACTUALLY BAD PRACTICE. INSTEAD WE SHOULD JUST SSH TO PATRICK.
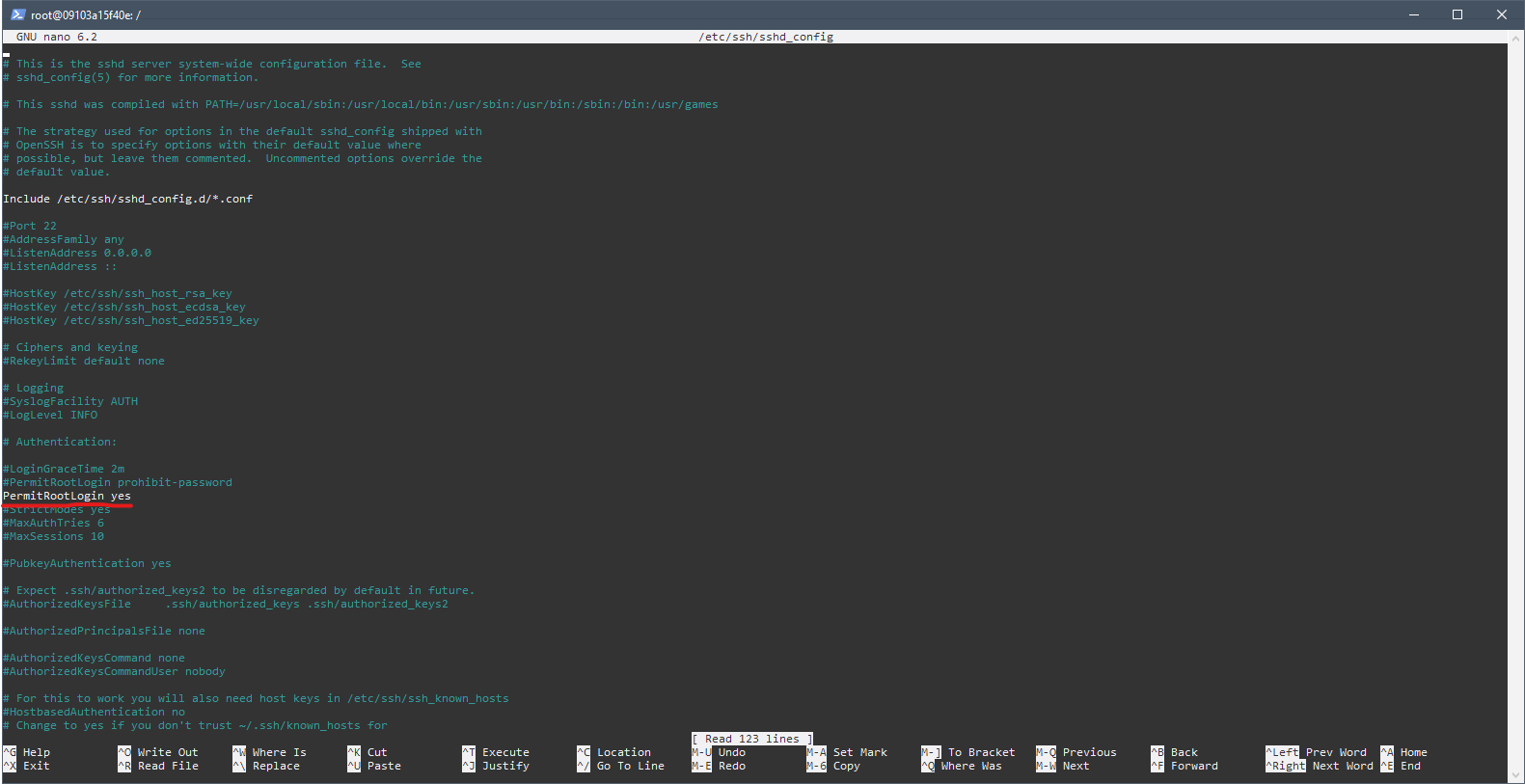
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Add PermitRootLogin yes under the Authentication section.
If you’re SSH server was running while doing this, you will need to restart the SSH service to apply the changes.
service ssh restart
Alternatively, to SSH to patrick,
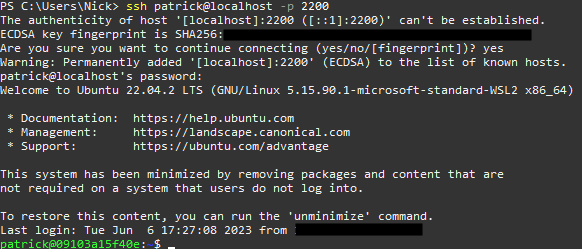
ssh patrick@localhost -p 2200
and if this is your first time connecting, you will see the message in the image below.
4. Connecting to the container via SSH from anoter machine
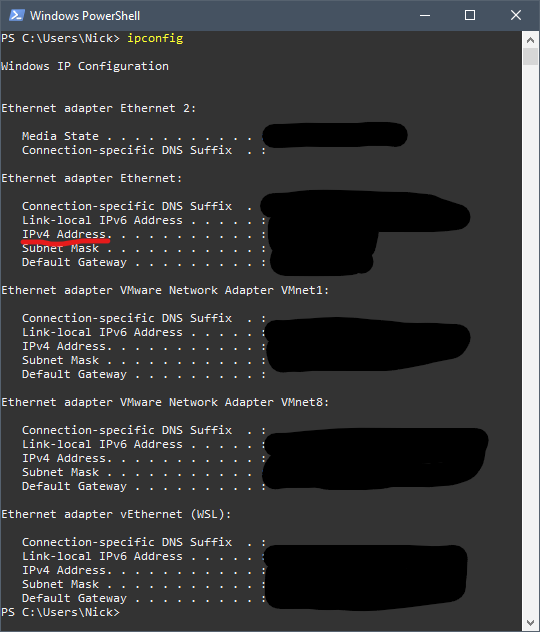
Ideally, we want to be able to SSH to the container from a machine other than our host. To do this, we will need to find the IP of the host machine. Into powershell type
ipconfig
and take note of the IPv4 address. Note: If the IP address of your host machine is dynamic, this will change over time. In this case you will need an additional service to handle this. I will not be covering this in this tutorial.
Now to connect to the container from another machine, type
ssh patrick@HOST_IP -p 2200
and you should be prompted for patrick’s password. Once entered, you will be connected. Note: Depending on the administrator settings of your host network of your host machine, you may need to VPN into the host network first.
5. Conclusion
In this tutorial we showed how to make a new user, install openssh-server, and connect to a Docker container via SSH. This is useful for remote development and testing.